On December 31, 2025, Governor Newsom signed Executive Order N-38-25, extending the application period for streamlined environmental review of certain qualifying vegetation management projects that reduce wildfire risk. Building on the March 2025 State of Emergency Proclamation (EP) that suspends numerous state environmental statutes and regulations for critical, near-term projects under 3,000 acres that comply with statewide environmental protection measures, the new Executive Order allows applicants to “initiate” projects, which means to at least submit a proposed project’s application for approval, through May 1, 2026. As emphasized in the associated press release, the rainy season offers an important seasonal opportunity to safely complete vegetation management activities, especially prescribed fire treatments under reduced wildfire risk conditions. The extension will enable land managers across the state to expedite key fuels reduction projects to reduce risk to communities, forests, and critical infrastructure.
This extension is meant to create a bridge to a durable, long-term regulatory framework for forest health and fuels reduction, according to the Governor’s press release. Recommendations for the long-term environmental review and regulatory compliance approach are being developed by the California Wildfire and Forest Resilience Task Force to be included in its upcoming Draft 2026 Action Plan update. A preview of the update was presented at the December 2025 Task Force meeting.
Here, we discuss what projects are eligible for the suspension of state environmental laws and how to apply.
The Governor’s March 2025 State of Emergency Proclamation
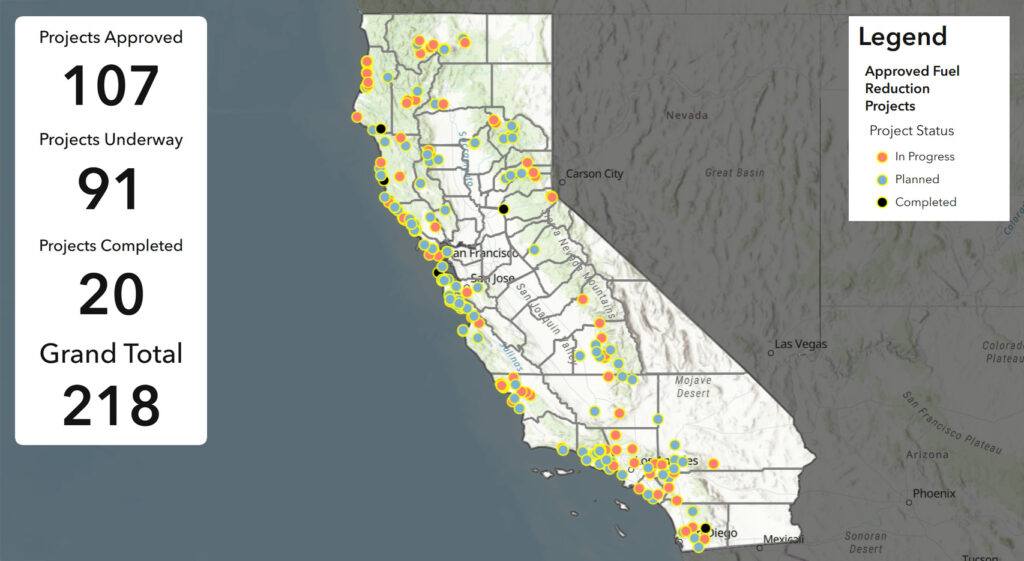
In March 2025, Governor Newsom issued a State of Emergency Proclamation to expedite critical, near-term fuels reduction projects that protect communities and reduce severe risks of catastrophic wildfire. The EP suspends CEQA requirements, as well as requirements under several state environmental statutes and regulations (including the California Coastal Act and the California Endangered Species Act), for fuels reduction projects under 3,000 acres that have as a primary objective at least one of the following six specific activities: (a) remove hazardous, dead, and/or dying trees; (b) create strategic fuels breaks; (c) build community defensible space; (d) establish safer travel routes or reduce roadside ignitions; (e) conduct prescribed fire/cultural burning; and (f) maintain previously established fuels reduction projects. Notably, a commercial timber project may also qualify for suspension under the EP, as long as it has as a primary objective one of these wildfire risk reduction activities and the commercial component is carried out pursuant to the Forest Practice Act and Rules under an approved harvest document. As of 1/6/2026, over 200 projects across California have been approved using the EP suspension, as shown in the below image of the EP Approved Projects Dashboard.
Use of the EP requires adherence to a November 2025 Statewide Fuels Reduction Environmental Protection Plan, which establishes best management practices and measures to minimize impacts to environmental resources when completing fuels reduction projects that are authorized under the EP suspensions from state environmental requirements. The Environmental Protection Plan streamlines and simplifies the substantive requirements that would otherwise govern fuels reduction projects through the normal regulatory process, covering protection of resources including tribal and cultural resources, riparian and water quality, and fish and wildlife species and their habitat. Recognizing that the EP suspends only specific state environmental laws, all relevant federal environmental statutes and regulations still apply, including the National Environmental Policy Act and the Endangered Species Act.
Applicants may submit project details using the online web portal through May 1, 2026, and will be notified within as few as 30 days if their application has been approved. Projects must begin implementation by October 15, 2026, and must be completed within two years of initiating groundwork. Implementation of projects funded by some state grant programs, including CAL FIRE Wildfire Prevention and Forest Health Grants and some Prop 4 programs, may be extended for up to five years from initiation. Maintenance treatments are subject to the same project timelines, so any additional treatments that address regrowth needed beyond the suspension time frame must comply with all applicable statutes outside of the EP suspension process (e.g., use an applicable CEQA exemption or the California Vegetation Treatment Program [CalVTP] Program EIR for CEQA compliance).
The year 2025 was dynamic with regard to regulatory requirements for environmental review of fire fuels treatment projects. In an upcoming AscentShare, we will provide a comprehensive recap of new CEQA exemptions, the CalVTP update, and other efficient state and federal environmental compliance pathways that emerged in 2025.
Please reach out to Katie Flahive, Lara Rachowicz, or Ted Thayer at Ascent with any questions about using the Emergency Proclamation to fast-track critical fuels treatment projects.